This article is an overview of satellite GNSS and CubeSat GPS receiver technologies available on the global marketplace. If you are familiar with this technology and would like to skip down to view the product listings, please click here.
There is growing demand for Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers that enable small satellites to achieve attitude and orbit control, orbital transfers, and end-of-life deorbiting.
In this article we provide a gentle primer to the topic of selecting a smallsat or CubeSat GPS receiver for a satellite mission and give an overview of some of the navigation and positioning products making waves in the global marketplace for space.
In the next few sections we take a brief look at how GPS receivers work and discuss what key performance characteristics need to be taken into account when selecting a product for your operation.
Introduction
Selecting the most appropriate CubeSat GPS receiver, or small satellite version, can be a tricky challenge.
The rapid growth of the NewSpace sector has led to greater use of modular components and several manufacturers are now producing CubeSat GPS receivers as independent products.
Selecting the right GPS receiver is important for ensuring the ease of operations of your satellite.
In this article, we look at some of the factors that should be taken into account to make this decision. We also provide an overview of a number of GPS receivers on the market, all of which are listed on the satsearch platform to help you select the best option.
GPS receivers are ubiquitous in many ground-based applications, from large-scale industrial transport navigation systems to fitness trackers and smartphones. However, using GPS receivers in space is a much more challenging task compared to normal terrestrial use.
Most terrestrial applications use Commercial Off The Shelf (COTS) components designed for specific operations and featuring typical characteristics needed for ground-based use. The difference between such uses and space-based GPS is not just in the components used but also in the software embedded, as GPS receivers made for terrestrial use typically are not tuned to accommodate the large variations in the received signal Doppler frequencies that are usually the case with satellites orbiting the Earth.
Aside from such technical limitations there are also regulatory issues such as the requirements set by the International Traffic on Arms Regulations (ITAR) which do not allow GPS receivers to provide navigation outputs after they exceed the ITAR limits of 60,000 feet and 1,000 knots. Therefore, GPS receivers often come with export control restrictions that depend on the end-user requirements. Be sure to check with the suppliers if they are able to actually serve you before considering testing a particular GPS receiver at the design stage.
Despite the limitations GPS receivers have been shown to be very useful for a range of in-orbit processes such as:
- Precise orbit determination
- Onboard time synchronization and geocoding of payload information
- Autonomous orbit control and manoeuvre planning
- Spacecraft formation flying
- Onboard attitude determination
Key performance criteria
Now that you’re armed with the knowledge of what a GPS receiver needs to do you can make an informed decision from the available products, based on your required performance characteristics.
Some of the potential key specifications and performance criteria to evaluate for each product are:
- Number of channels
- Number of antennae
- Frequencies
- Position accuracy
- Velocity accuracy
- Update rate
- Power consumption
- Time-To-First-Fix (TTFF)
These provide a snippet of the technical details that are necessary to evaluate as part of your selection process. In addition, there are the typical criteria for any major purchase such as; cost, delivery time, supplier reputation and location (particularly regarding any export controls, as mentioned above), contract details and maintenance conditions to take into account.
Finally, it’s important to note that selection of a GPS receiver for your satellite is an iterative process, as is the case for virtually every other component of your overall system.
Smallsat and CubeSat GPS receivers on the market
In this section, you can find a range of GPS receivers available on the global market. These listings will be updated when new gps receiving products are added to the global marketplace for space at satsearch.co – so please check back for more or sign up for our mailing list for all the updates.
We have also put together overviews of X-band transmitters, S-band transmitters and S-band antennas to help you evaluate additional satellite communications systems.
Get more information on all products listed at the click of a button
We can help you access quotes, lead times, or any other information from all of the suppliers listed below (and more) with our simple, free tender system. Just share your details with us and wait for the responses to arrive in your inbox.
The AAC SpaceQuest GNSS-701 - Satellite GNSS Receiver is a space-qualified GPS receiver with an improved core and expanded interface board. The system is designed to offer higher accuracy, compatibility, and functionality.
The Accord ACC-GPS-NANO is a miniaturized GPS-GAGAN receiver designed specifically for small satellite applications in LEO. The receiver supports 16 acquisition and tracking channels to enhance the time to first fix under cold start. The NMEA protocol and the proprietary protocol provides the information needed during the satellite motion.
The Accord ACC-GPS-NANO-NR is a GPS-SBAS receiver with a 32-Channel GPS-SBAS engine to determine orbital position and time designed for LEO missions.
The Accord ACC-GPS-NAVIC-NANO is a miniaturized GPS-NAVIC receiver designed specifically for satellite applications in LEO. The receiver supports 25 acquisition and tracking channels to enhance the time to first fix under cold start. The NMEA protocol and the proprietary protocol provides the information needed during the satellite motion. The receiver is designed to work with an active GPS antenna. The power to the antenna is fed by the receiver itself.
The Accord Navika-251-HD is a GPS-GLONASS-SBAS receiver module designed for sounding rocket application. Navika-251-HD supports the NMEA-0183 message protocol to communicate the location information. Navika-251-HD also provides an accurate time pulse with associated GPS / UTC time stamping along with the location data.Navika-251-HD can be interfaced with either an active or passive GPS antenna.
The Accord ACC-GPS-NANO-DR is a Dual Redundant GPS-SBAS receiver consisting of a pair of 32 Channel receivers independent of each other. The system is used to determine orbital position and time and is designed for LEO missions. The two independent receivers has a common antenna interface and a power divider to split the GPS signals.
The Accord ACC-G3IR-LV is a miniature high performance GPS-GLONASS-NAVIC-SBAS Receiver designed specifically for Launch Vehicle applications. The system supports 40 channels (16 GPS, 14 GLONASS, 7 NAVIC, 3 SBAS).
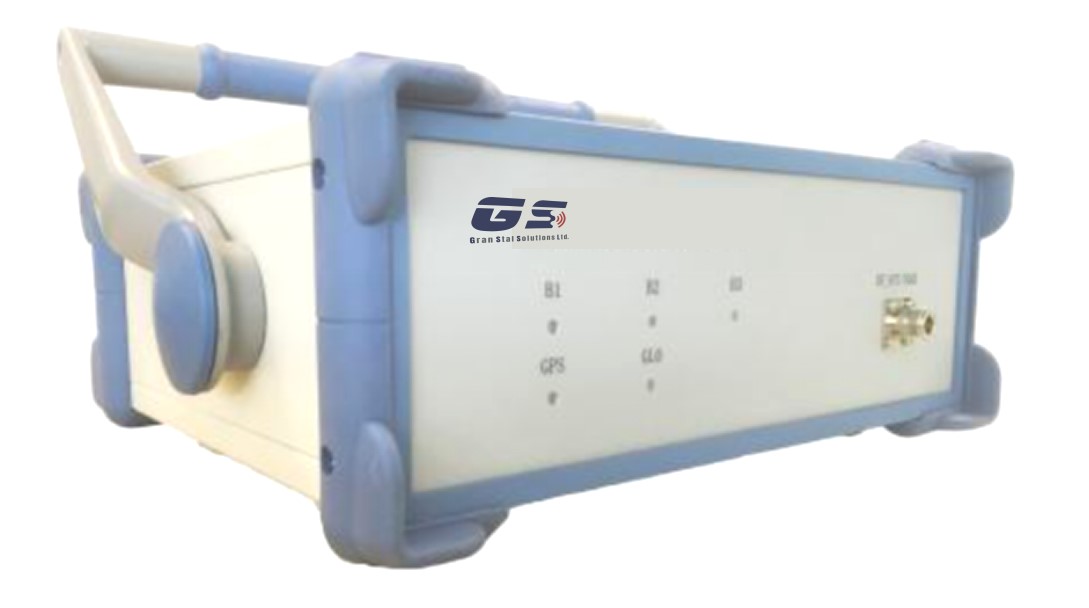
The GranStal GS-FN28Q GNSS OEM board is the latest generation receiver powered by the most advanced algorithms for robust and accurate positioning. The GS-FN28Q integrated GNSS receiver offers full Precise Positioning Service (PPS) accuracy. Powered by state-of-the-art technology, simultaneous GPS- L1/Beidou-B1 operation provides real-time ionosphere corrections for further accuracy enhancements.
The GS-FD38A GNSS OEM boards is Gran Stal’s latest generation receiver powered by the most advanced algorithms for robust and accurate positioning. Derived from the field-proven, the 48-channel GS- FD38A GNSS receiver is designed with a dual-frequency, all-in-view receiver capable either as a stand-alone system or integrated with an Inertial Navigation System (INS).
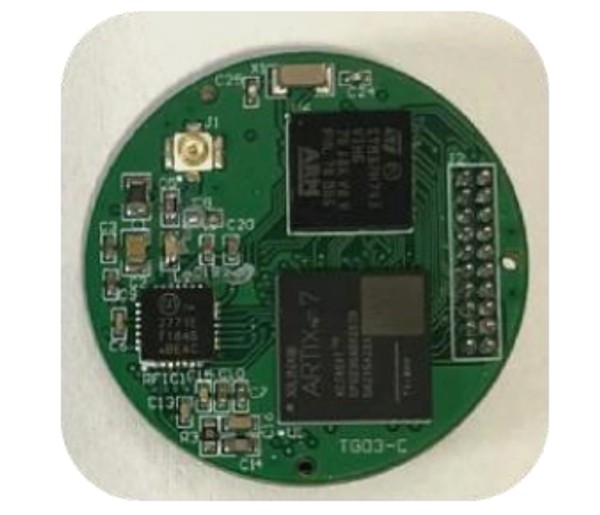
The GS-3T-Nano GNSS Receiver is designed with a light weight for micro and pico satellites. The SOC chip is used as the core chip for navigation solving and processing, with the performance of positioning, orbiting, timing, and dual frequency raw measurement for LEO and MEO.
The GranStal Solutions GS50 GNSS Receiver consists of two configured GNSS receivers; a GPS+GLONASS and a GPS+BD2-B1 dual-mode receiver, either by replacing the front end of the receiver filter and built-in embedded program to perform a state change. The system enables rapid hot start location and is designed for accuracy and low power consumption.
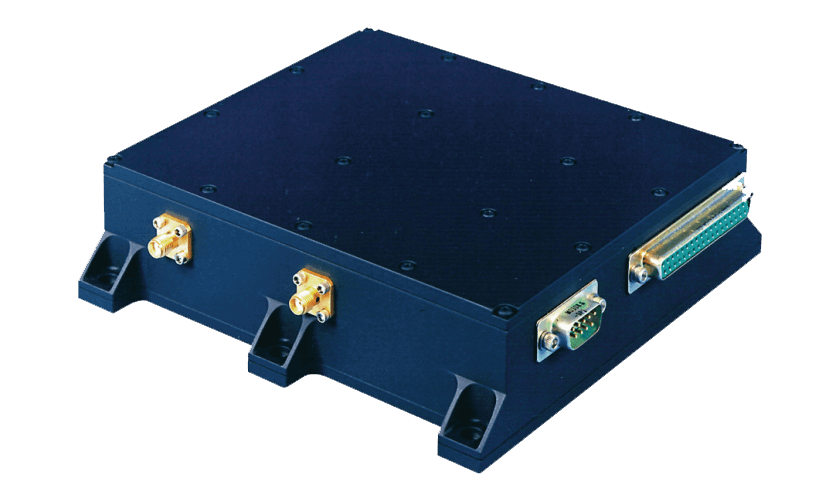
The NSS Gemini SR28 GPS Receiver range is L1 frequency GPS Receivers which utilizes a heritage GPS chipset. Targeted towards low-cost SmallSat constellations, it allows for space altitude and velocity use cases. The Gemini-SR5 operates from a 5V supply voltage while the Gemini-SR28 operates from an unregulated 28V supply voltage incorporating latch-up protection/detection and a watchdog timer for increased reliability and robustness.
The NSS Gemini SR5 GPS Receiver range is L1 frequency GPS Receivers which utilizes a heritage GPS chipset. Targeted towards low-cost SmallSat constellations, it allows for space altitude and velocity use cases. The Gemini-SR5 operates from a 5V supply voltage while the Gemini-SR28 operates from an unregulated 28V supply voltage incorporating latch-up protection/detection and a watchdog timer for increased reliability and robustness.
Spacemanic's Celeste - the GNSS Receiver - is a multi-GNSS receiver module suitable for nanosatellite position acquisition and determination. The system has a plug-and-play design and is compatible with a wide variety of CubeSat components.
The SkyFox Labs piNAV-NG/FM (Flight Model) is a GPS Receiver designed for CubeSats. It is a long-term optimized CubeSat GPS Receiver with firmware based on many years of orbital operations heritage intended for modern satellites, CubeSats, and a majority of scientific/business/university projects, where the satellite development team requires a module with limited size and power budget.
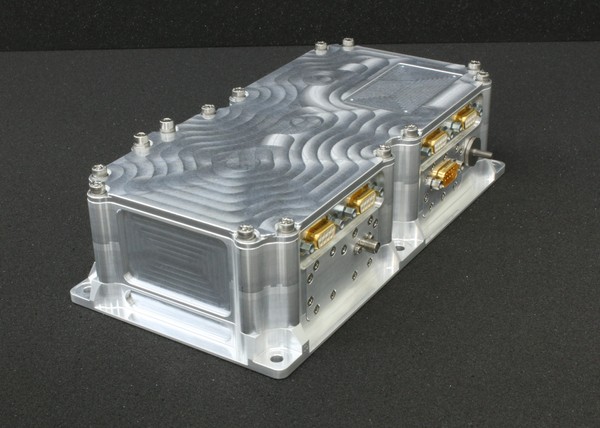
The GPS-110 is a reliable computation unit with two GPS receivers and an RS422 interface for measuring the position and velocity in orbit. The fully redundant GPS receivers are able to work independently with two active GPS antennas and provide one position and velocity update per second.
This receiver is form-fit-function compatible with the OEM615 and 617 variants which are legacy receivers in space.
The SpacePNT NaviLEO-POD1 is a high-performance solution delivering sub-decimeter-level positioning and timing accuracy for LEO missions.
The SpacePNT NaviGEO is a high-performance solution designed for launcher upper stages and in-orbit servicing vehicles.
The Syntony SoftSpot™ is a real-time software GNSS receiver used for deep signal analysis of the received signal. It displays all issues like abnormal C/N0, unrealistic PVT solutions, errors inside the navigation message, satellites out of order, etc. SoftSpot takes I/Q samples from the RF Stage at an intermediate frequency and can process signal correlation either by software or through FPGA correlators.
The Syrlinks EWC40 : G-SPHERE-S GNSS Software Receiver is a product under development for space applications.
Thanks for reading! If you would like any further help identifying a GPS receiver for your specific needs, please file a request on our platform and we’ll use our global network of suppliers to find an option.