Deployable mechanisms can bring huge flexibility and performance increases to space hardware.
The ability to deploy large antennas, solar arrays, cameras, and other equipment outside of the initial system’s envelope can enhance the primary functions and add new capabilities in the mission plan.
In this article we discuss some of the core functions and benefits of deployable mechanisms, then share details on a variety of systems available on the commercial market.
Introduction to deployable mechanisms for space missions
Deployables are a broad category of technologies that either physically move themselves, or enable other components and subsystems to move while in orbit.
One of the limits of satellite performance is the amount of hardware that can be packed into the physical volume of the system.
Although launch costs continue to decrease, getting a system to orbit is still expensive and complicated. So satellite designers try to ensure that their systems are compact and have a standardized 3D shape – usually a cube or rectangle – to more easily fit into the launch vehicle (LV) and deployer.
Then, to overcome the physical limit of the system’s outer envelope, deployable subsystems are incorporated which can open, move, and/or extend once the satellite has left the LV. Deployable mechanisms can also play a role in the act of dispensing the satellite from the LV.
Some of the most well known examples of subsystems that can be deployed in space are:
- Solar arrays – which open and expand to collect more solar energy with the larger surface area,
- Antennas – that extend out of a satellite to increase the system’s communication capabilities,
- Cameras and sensors – enabling more advanced and versatile applications when utilized outside of the satellite’s main housing, and
- Booms and solar sails – to generate thrust (for satellite propulsion) and/or drag (for de-orbiting).
Space-rated deployable mechanisms are reliable actuators that enable the use of all of these subsystems, and more.
They are also widely used to secure sensitive components during launch and deployment, to avoid damage caused by the high vibrations.
Known as hold down and release mechanisms (HDRM); such components are very important for precise cameras for example, and have been used on missions at all scales, from picosats to large-scale exploration spacecraft.
The advantages of deployable mechanisms
High-quality deployable mechanisms typically have a number of advantages over traditional integrated components in subsystems which are custom-built for a specific function. Mechanisms for deployable space systems are:
- Field-resettable – deployable mechanisms can often be reset while in space. This can open up new mission applications and reduce risk.
- Redundancy – as well as being field-resettable, advanced deployables also typically incorporate redundant components to serve as back-ups should deployment fail.
- Versatile – modular deployables can be used in various different applications and subsystems. This gives mission designers greater flexibility to create plans involving deployed subsystems that might otherwise not have been possible.
- Simplified testing and qualification – qualifying any deployable system is a challenge (as covered in our podcast with deployables manufacturer DCUBED) so being able to use pre-qualified, TRL9, systems is a significant advantage.
Of course, every space component will have trade-offs. Deployables might require changes to engineering plans, an increase in power requirements, or greater thermal protection, but such impacts are likely to be small given the size and nature of such systems.
Next let’s take a look at a range of deplyable mechanisms on the global market.
Deployable mechanisms on the global marketplace
In the list below you can see a range of individual deployable mechanisms for various applications and subsystems. Click on any of the boxes to open a page with more detail on the mechanism or supplier that you are interested in.
From these pages you can submit requests for quotes, documents, or further information by the supplier, and we’ll handle the request on your behalf (find out more about how this works here).
If you want to shortcut this process, or need some assistance refining your requirements, you can instead rapidly submit an open tender and our expert procurement team will get back to you ASAP.
The COMAT SADM 200 is a plug & play Solar Array Drive Mechanism for small satellites to optimize onboard power generation.
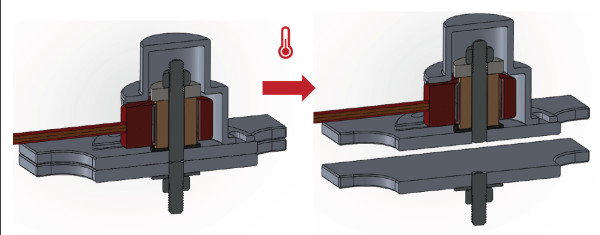
The DCUBED Nano Pin Puller (nD3PP), available in Stainless Steel or Aluminum-Titanium, is a Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) based release actuator that locks sensitive equipment during launch and safely releases it on orbit. It is one of the smallest, yet powerful space-qualified HDRM solutions on the market. Moreover, it is easily field-resettable, easy to use, and readily available as a COTS part.
The DCUBED Nano Release Nut (nD3RN), available in Stainless Steel or Aluminum-Titanium, is a Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) based release actuator that secures sensitive equipment during launch and safely releases it on orbit. It is one of the smallest, yet powerful HDRM solutions on the market. Moreover, it is easily resettable, easy-to-use, and readily available as a COTS part.
The DCUBED Nano SmartPack Release Nut (nD3SP) is a Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) based release actuator that locks sensitive equipment during launch and safely releases it on orbit. It is one of the flattest, yet powerful HDRM solutions on the market. Moreover, it is easily resettable, easy to use, and readily available as a COTS component.
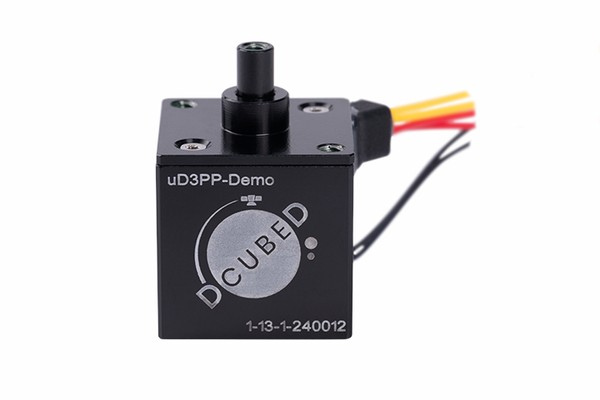
Straight forward release actuator locking mission-critical subsystems during launch and releasing them safely on orbit. The DCUBED Micro Pin Puller (uD3PP) is a Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) based release actuator that locks sensitive equipment during launch and safely releases it on orbit.
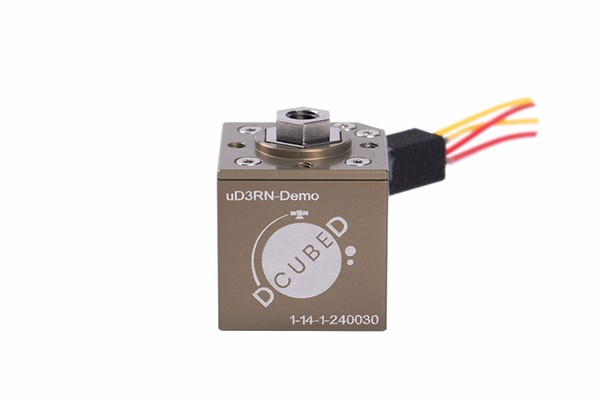
The DCUBED Micro Release Nut (uD3RN) is a Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) based release actuator that locks sensitive equipment during launch and safely releases it on orbit. It is one of the smallest, yet powerful HDRM solutions on the market. Moreover, it is easily resettable (on-ground, in-space), easy to use, and readily available as a COTS part.
The DHV Technology MicroSADA-10 is designed for 6U and 12U CubeSats. It is customizable to include Solar Array Drive Mechanisms (SADM) and Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) modules in one single device. It is designed for platforms with a height of 10 mm.
The DHV Technology MicroSADA-18 is designed for 6U and 12U CubeSats. It is customizable to include Solar Array Drive Mechanisms (SADM) and Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) modules in one single device. It is designed for platforms with a height of 18 mm.
The EOSOL Antenna Pointing Mechanism (APM) is a 2-axis antenna pointing mechanism for small or flat antennas around 30cm. The APM system is compact and ready to mount on flat or small reflector antennas. The antenna pointing mechanism has two pointing axes: azimuth and elevation. They are controlled by stepper motors and encoders for accurate pointing. The three different modes of operation enable accurate pointing of LEO, MEO, and GEO targets in both static and dynamic operations.
The Oxford Space Systems AstroTube Max is based on a flight-proven, novel deployment mechanism and a nested stack of outer telescopic tubes. This results in a low complexity, highly versatile boom system for a variety of mission requirements. The AstroTube Max can be both partially and fully deployed as well as retracted. The addition of rifling allows the boom to offer unlimited rotation at any point during the deployment/retraction.
The Arquimea HDRM REACT 5KN & DEM is a Hold-Down and Release Actuator Mechanism and a deployment mechanism for solar arrays, antennas, thrusters, reflectors. REACT is a low-shock Hold-Down & Release Actuator to firmly hold the payload during transportation and launch and also to release it later by electrical activation. DEM is designed mainly for the solar array deployment in small-and mid-size satellites.
The Nimesis GRIPPER - Shockless Hold Down Release Actuator is a lightweight and compact actuator designed for space applications. It is used as a solution for the locking/unlocking and release of space mechanisms. GRIPPER is compatible with a wide range of satellites and space systems. It also consists of shockless actuation and has the capability to operate in temperatures ranging between -80°C to +120°C.
The Nimesis TRIGGY - Launch Lock Device is a compact actuator designed for the release, locking/unlocking, and dismantling process. TRIGGY is compatible with Hold Down Release Mechanisms (HDRM) and has a trigger time between 30 to 300 seconds. It can operate in temperatures ranging between -120°C to +120°C. The product also consists of Reset and Tensioner tools.
The Sierra Space PP-35055 Pin Puller is a remotely resettable mechanism that provides high retraction force. The heart of the PP-35055 is an EH-35055 high force High Output Paraffin (HOP) actuator providing a maximum of 350 lbf of retraction force to the output pin. The pin puller is fully resettable and contains an integral binary latching mechanism to provide high-shear and high retraction force.
Sierra Space's IH-5055/-10055 HOP actuators are electrically powered resettable devices generating high-force and long-stroke linear motion.
The Everlight Microsatellite Secure and Release Mechanism is a mechanism for space structures to be secured during launch and released with precision and reliability on-orbit. Release is low-impact and separation is achieved without using initiators or pyrotechnics. The devices are flight-proven and is designed to be high-reliable, compact in size, lightweight, and versatile. The mechanism can be reset for ground testing.
The Arquimea HDRM Deployment Mechanism (DEM) is a Hold-Down and Release Actuator deployment mechanism for solar arrays, antennas, thrusters, reflectors. DEM is designed mainly for the solar array deployment in small-and mid-size satellites.
The Revolv Space SARA is an autonomous & fail-safe Solar Array Drive Mechanism for smallsats, including actuation system, electronics, & sun sensors.
Thanks for reading! If you need any further help identifying the right deployable mechanism for your specific needs, please share your specifications with us and we’ll use our global network of suppliers to find options.
Have you noticed that your company isn’t included in this article?
Click here to find out the benefits of claiming your free profile on satsearch.
Once your pages are live, just send us an email and we can discuss showcasing your products to the global space engineering community on this page.